- Pulsus Bigeminus Definition
- Pulsus Bigeminus Meaning
- Pulsus Bigeminus Definition
- Pulsus Bigeminus Etiology
- Pulsus Bisferiens Waveform
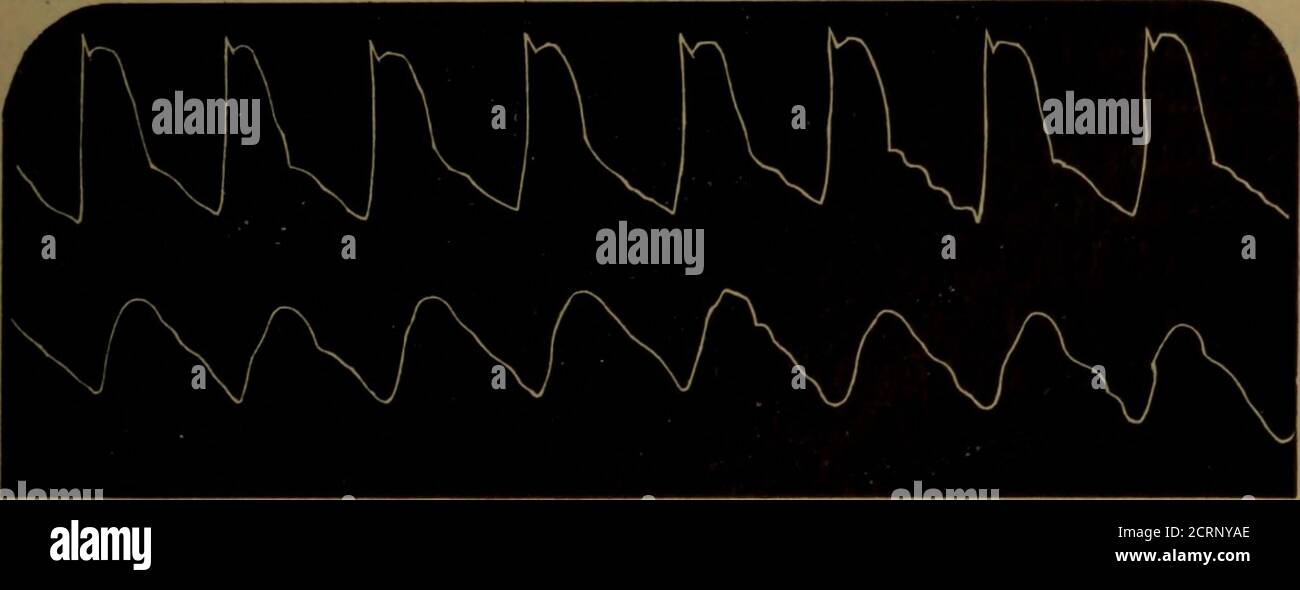
Pulsus bigeminus is a cardiovascular phenomenon characterized by groups of two heartbeats close together followed by a longer pause. The second pulse is weaker than the first. Look for a pattern of what appears to be a relatively normal QRS complexes, each followed by a smaller, abnormal one. The peripheral pulse associated with such episodes is known as pulsus bigeminus. The most feared complication is its potential to develop into ventricular fibrillation and asystole. Immediate post-operative ventricular bigeminy in a patient operated for ovarian cystectomy: a case report.
(redirected from Pulsus bigeminus)Also found in: Encyclopedia, Wikipedia.
Pulsus bigeminus (195103000); Bigeminal pulse (195103000) Recent clinical studies. Extensive subcutaneous emphysema and hypercapnia during laparoscopic cholecystectomy: two case reports. Abe H, Bandai Y, Ohtomo Y, Shimomura K, Nayeem SA, Idezuki Y. Pulsus bigeminus is a cardiovascular phenomenon characterized by groups of two heartbeats close together followed by a longer pause. The second pulse is weaker than the first. Look for a pattern of what appears to be a relatively normal QRS complexes, each followed by a smaller, abnormal one.
pulsus
[pul´sus] (L.)pulse
(pŭls),pulse
(Pulsus Bigeminus Definition
pŭls)Synonym(s): pulsus.
Want to thank TFD for its existence? Tell a friend about us, add a link to this page, or visit the webmaster's page for free fun content.
Link to this page:
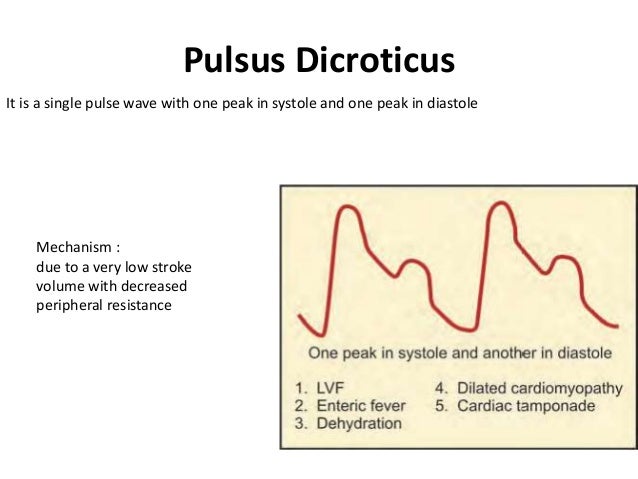
Pulsus bigeminus is a cardiovascular phenomenon characterized by groups of two heartbeats close together followed by a longer pause. The second pulse is weaker than the first. Look for a pattern of what appears to be a relatively normal QRS complexes, each followed by a smaller, abnormal one. The smaller beat is palpated as either a missing or an extra beat, and on EKG resembles a PVC.[1] These PVCs appearing every other beat are also called extrasystoles.
This phenomenon can be a sign of hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy or of many other types of heart disease (see list below). Other causes include digitalis toxicity, induction of anesthesia,[2] placement of surgical instrumentation into the thorax or as a benign, temporary phenomenon.
In Pulsus Bigeminus not all of the conducted electrical activity will elicit sufficient ventricular contraction to produce a palpable pulse. This is important for two reasons. One, an ECG may give a ventricular contraction rate that does not correspond to the palpated pulse rate. Secondly, because not all beats are being conducted, patients may present with symptoms of low output heart failure, e.g. Dizziness, shortness of breath or hypotension, even with a normal ECG.
Cause[edit]

Causes Include:
- Electrolyte imbalance e.g. Hypo or hyperkalemia
- Betablocker therapy
- Destruction or degeneration of the cardiac conduction system or heart muscle cells
- Infection
Pulsus Bigeminus Meaning
A doctor can discriminate pulsus bigeminus from pulsus alternans by auscultating the heart.
Management[edit]
Pulsus Bigeminus Definition
Management includes looking for and removing underlying cause, including medicines (such as a Calcium Channel blocker) and inotropic therapy to return cardiac output back to normal. If highly symptomatic over a longer period ablation therapy may be the only viable option.
See also[edit]
Pulsus Bigeminus Etiology
References[edit]
- ^Anand, Nidhi; Manish Anand; Alok Vardhan Mathur; Madhukar Maletha; SK Ghildyal (2010-02-03). 'Intra-operative ventricular bigeminy: Can retractor be a cause'. Journal of Anaesthesiology Clinical Pharmacology. 26 (4): 569–570. Retrieved 2012-05-16.
- ^ROLLASON, WN; D. J. HALL (March 1973). 'Dysrhythmias during inhalational anaesthesia for oral surgery'. Anaesthesia. 28 (2): 139–145. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2044.1973.tb00305.x.
Pulsus Bisferiens Waveform
