- Samuel Hunter Christie was a British scientist and mathematician.He was particularly interested in magnetism, studying the earth's magnetic field and designing improv.
- The linear model correctly predicts the MOSFET behavior for small drain-source voltages, where the MOSFET acts as a variable resistor. The quadratic model includes the voltage variation along the channel between source and drain. This model is most commonly used despite the fact that the variation of the depletion layer charge is ignored.
- Tutorial on Field Effect Transistor FET as a switch. Using JFET as shunt and series switch, P-Channel JFET as a Switch, MOSFET as switch.
- Variable Resistor Purpose
- Multiturn Preset Resistor
- Resistor
- Mosfet As A Variable Resistor
- Variable Resistor Connections
- Mosfet As Variable Resistor Formula
- Best Mosfet As A Variable Resistor
JFET Variable Resistor
You can use the fact that the MOSFET can be used as a voltage-controlled resistor, to make a voltage-controlled potentiometer. Consider the voltage divider shown in Fig. R 1 is a conventional, fixed resistor, whereas R 2 is a variable resistor. If a voltage v XY is applied to the circuit as shown, the output voltage v ZW will be v R RR.
CIRCUIT
JFET_VARIABLE_RES1.CR Download the SPICE file
JFET_VARIABLE_ATTEN1.CR Download the SPICE file
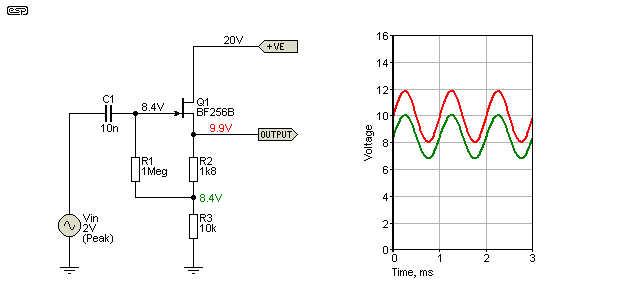
Some designs call for a variable resistor such as variable gain amplifiers, attenuators and some guitar effect boxes. The main goal here is device whose resistance is some function of bias voltage. One such device is your basic JFET. For small signals, where the device operates in the linear (or ohmic) region, the resistance between the Drain and Source terminals (Rds) decreases as the gate voltage increases.
IV CURVES
How can you determine the JFET resistance versus bias voltage? Nothing tells the story like the slope of the IV curve. Here's the basic circuit to develop these insightful graphs.
* GATE AND DRAIN VOLTAGE
VG 1 0 DC 0
VD 2 0 DC 0
J1 2 1 0 J2N5952
*
* Nested DC sweep
.DC VD -0.05 0.05 0.1 VG -1.75 0 0.25
The file includes an essential line - the nested DC sweep command.
Variable Resistor Purpose
.DC V1 Start Stop Incr V2 Start Stop Incr
You define how the test voltages V1 and V2 will start, stop and increment. Then, for each V1 voltage point, V2 will sweep through its entire range from start to stop. This comes in handy where the drain (VD) is swept through its range for every gate bias voltage (VG).
Multiturn Preset Resistor
CIRCUIT INSIGHT Run a DC analysis of the 2N5952 JFET in the JFET_VARIABLE_RES1.CIR and plot the drain current ID(J1). The drain is only swept from -50mV to +50mV. You should see a nice family of curves representing the Id as a function of Vd for each value of Vg. The slope of each VI curve represents the Drain-Source resistance. What is the minimum resistance? The smallest slope (resistance) can be approximated by Rds = 50mV/30uA = 1.66k ohms. The largest slope is Rds = 50mV/250uA = 200 ohms. This shows the range of resistance possible when sweeping the gate from -1.75 to 0V.
As warned earlier, this resistor-like operation applies only to small signals. What about larger signals? Increase the Vd sweep parameters to Start = -0.5V and Stop = +0.5V. What happens to the linearity of the IV plots?
VARIABLE ATTENUATOR
Here's an application of a JFET taken straight out of a National app note. The JFET implements a voltage attenuator as one leg in a voltage divider.
The voltage divider ratio is defined by Vo/Vs = R2'/(R1+R2') where R2' is actually the parallel combo of R2 and Rds. For this example, setting R1=10k and R2=100k defines a small attenuation, even when the JFET is OFF (very high resistance)
CIRCUIT INSIGHT The gate voltage VG ramps from -2V to 0V while a 100mV (1kHz) sine wave is applied to the divider input. Run a TRANSIENT ANALYSISs of JFET_VARIABLE_ATTEN1.CIR and plot both the gate voltage (V3) and the output voltage V(2). At what gate voltage does Rds begin conducting and attenuating the signal? Where does the max attenuation occur? You can estimate Rds by measuring V(2) peaks and solving the divider equation for R2.
UPCOMING TOPICS
In a future topic, we'll use the variable resistor as part of a popular guitar effects pedal called the phase shifter.
Resistor
SPICE FILES
Variable Resistor
Download the file or copy this netlist into a text file with the *.cir extension.
Mosfet As A Variable Resistor
Download the file or copy this netlist into a text file with the *.cir extension.
Variable Attenuator
© 2012 eCircuit Center
Variable resistor basics

variable resistors are used as volume control and also for other controls in radio and TV sets.They are also referred as 'pots'.For high power application fixed wire wound resistor and for low power application fixed carbon resistor of highvalue is used.

As shown in the figure, variable resistor will have three tags viz. two outer one and one at the center.A wiper makes contact with the track which is connected with center tag. Rotation of the spindle moves the wiper over the track which changes theresistance between the center tag and the end ones.slide type variable resistors will have straight track.
There are different types viz. linear and log.In linear type, change in resistance is proportional to angle. In log type, change in resistance at one end of trackis less than at the other for equal angular positions. Transformers 4 4k extinction download torrent.
Variable resistors are available with typical maximum values which include 10KOhm, 50KOhm, 100KOhm, 500KOhm and 1MOhm.These devices often referred as potentiometers are tuned as per resitance value needed using screwdriver.
Variable resistor is used for following functions:
• As rheostat to control the current in the electronic circuit.
• As voltage divider to obtain any voltage from zero to maximum of supply voltage.
Variable resistor manufacturers
Following are few of the reputed variable resistor manufacturers also referred as trimmers, potentiometers and rheostats.
1. vishay
2. Hindustan Electronic Components
3. Jameco Electronics
4. Mouser Electronics
5. Ohmite
6. CTS
7. NTE Electronics Inc.
8. Murata electronics
9. ACP
10. C & K Components
11. Nobel
12. Omite
6.4 properties of definite integralsap calculus. 13. TOCOS America
14. P3 America
RELATED LINKS
Variable capacitor
Variable resistor
Transformer basics and types
Ohm law
BJT vs FET
Diac vs Triac
JUGFET vs MOSFET
Analog vs Digital Multimeter
LED vs Laser
Microphone basics and types
Resistor basics
Electrolytic capacitor
Capacitor basics
Inductor basics
Transducer
Thermistor
Relay
Reed Switch
Photo Diode vs Photo Transistor
Battery
SCR or thyristor
Op-Amp
Halfwave rectifier vs Fullwave rectifier
RF and Wireless Terminologies
Variable Resistor Connections
Mosfet As Variable Resistor Formula
Share this page
Best Mosfet As A Variable Resistor
Translate this page
