Atomic Mass and Nuclear Binding Energy for Ar-37 (Argon)
The sum of mass of proton,electron and neutron (individual components) of an atom is atomic mass. Sources of Argon: Argon makes up 1% of the air and is isolated by removing nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and water from air. Argon is constantly being formed from the radioactive decay of K-40 (an isotope of potassium). Of radioactive potassium-40. World wide commercial production is around 700,000 tons per year.

Atomic Mass of Argon Atomic mass of Argon is 39.948 u. The atomic mass of aluminum is 26.98 amu. Aluminum is one of the lightest elements, making it ideal for construction, transportation and other commercial uses. Aluminum is a very common element, third in abundance only to silicon and oxygen.
Abstract
This document is part of the Supplement containing the complete sets of data of Subvolume A `Nuclei with Z = 1 - 54' of Volume 22 `Nuclear Binding Energies and Atomic Masses' of Landolt-Börnstein - Group I `Elementary Particles, Nuclei and Atoms'. It provides atomic mass, mass excess, nuclear binding energy, nucleon separation energies, Q-values, and nucleon residual interaction parameters for atomic nuclei of the isotope Ar-37 (Argon, atomic number Z = 18, mass number A = 37).
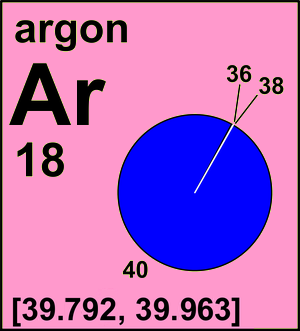
Atomic Mass Vs Atomic Number
Element Ar
Ar Atomic Mass In Kg
Nist Argon Ii Ver Argon I
- atomic mass;
- mass excess;
- nuclear binding energy;
- nucleon separation energy;
- Q-value;
- nucleon residual interaction parameter
